Google Scholar / GitHub / X / CV |
I am a Ph.D. candidate at University of California, Berkeley,
co-advised by Professor Yi Ma (EECS / HKU) and
Professor Meng C. Lin (Vision Science).
I received my M.Sc. at National Taiwan University (NTU).
|

UC Berkeley |

FAIR |

Adobe Inc. |

IIS, Academia Sinica |

NTU |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Project Page |
Abstract |
Bibtex |
Preprint |
PDF |
🤗 Huggingface Benchmark |
Code |
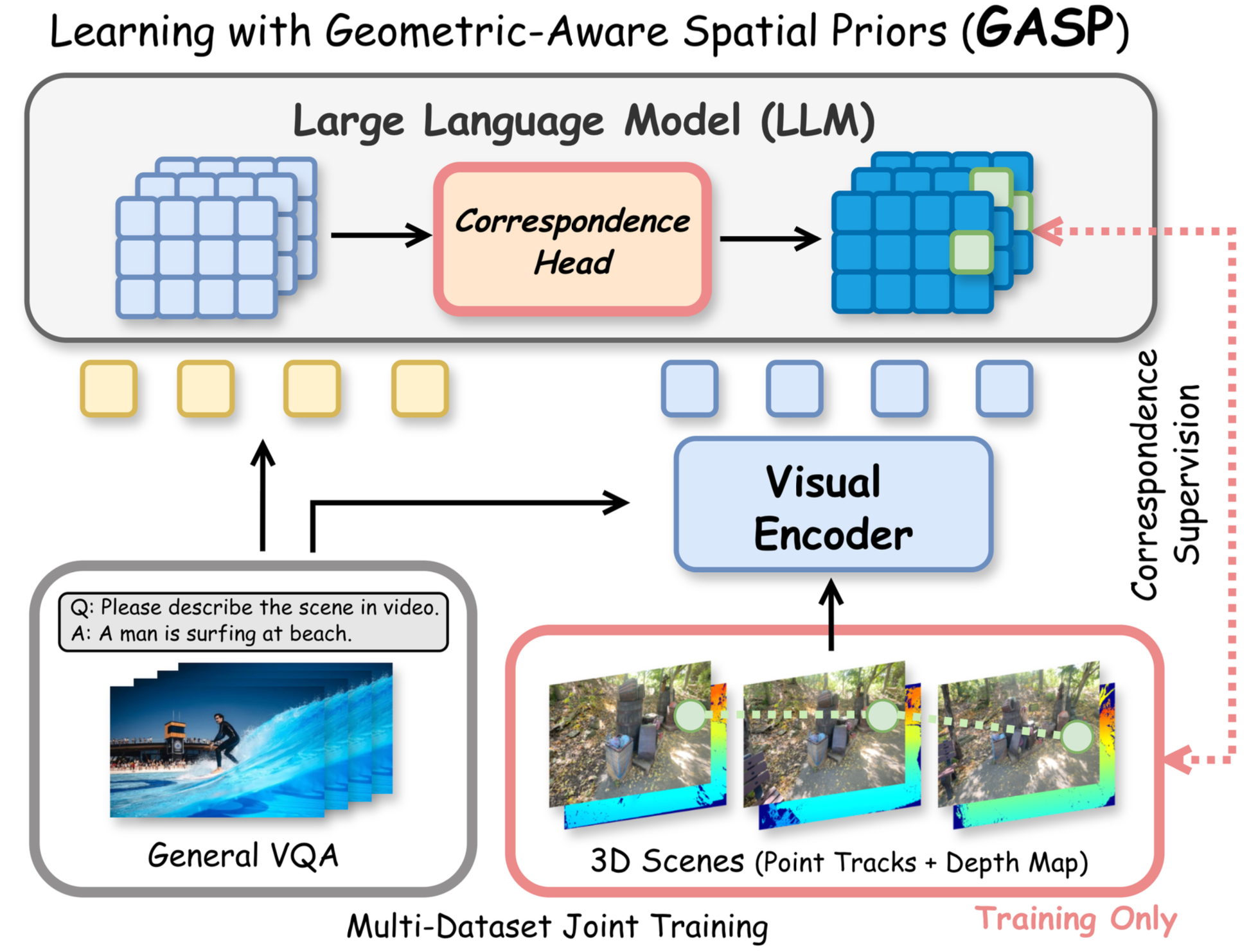
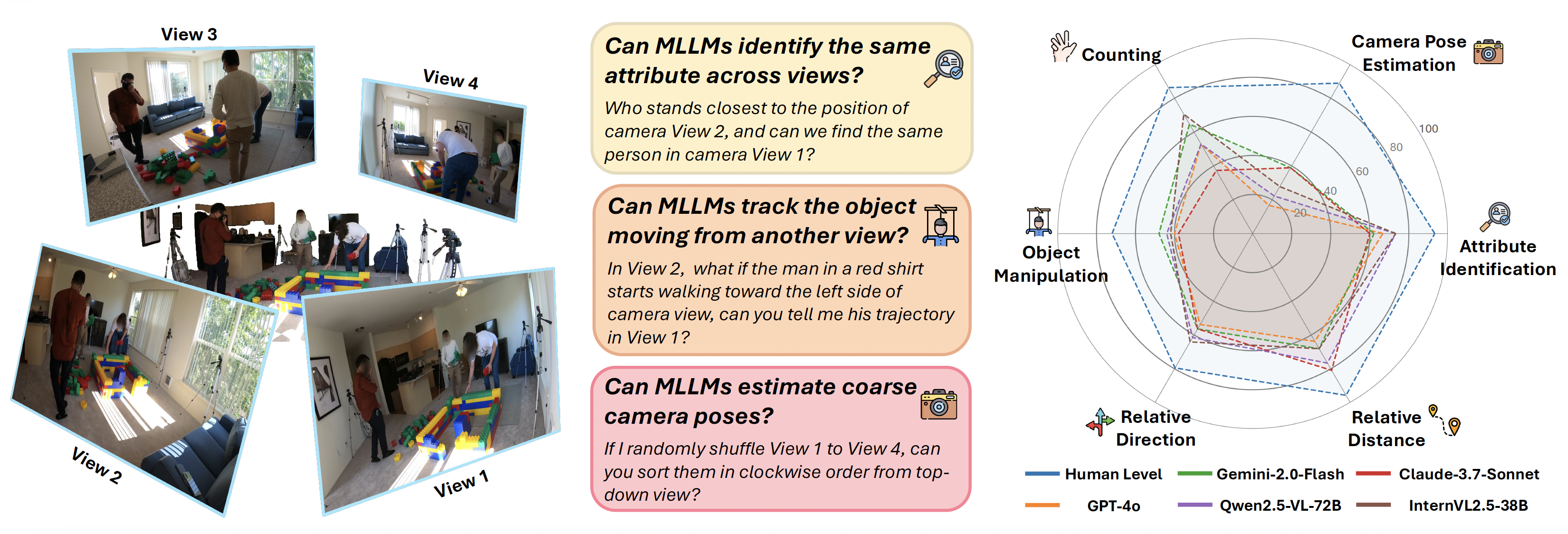
Multi-view understanding, the ability to reconcile visual information across diverse viewpoints for effective navigation, manipulation, and 3D scene comprehension, is a fundamental challenge in Multi-Modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to be used as embodied agents. While recent MLLMs have shown impressive advances in high-level reasoning and planning, they frequently fall short when confronted with multi-view geometric consistency and crossview correspondence. To comprehensively evaluate the challenges of MLLMs in multi-view scene reasoning, we propose All-Angles Bench, a benchmark of over 2,100 human carefully annotated multi-view question–answer pairs across 90 diverse real-world scenes. Our six tasks (counting, attribute identification, relative distance, relative direction, object manipulation, and camera pose estimation) specifically test model’s geometric correspondence and the capacity to align information consistently across views. Our extensive experiments, benchmark on 27 representative MLLMs including Gemini-2.0-Flash, Claude-3.7-Sonnet, and GPT-4o against human evaluators reveals a substantial performance gap, indicating that current MLLMs remain far from human-level proficiency. Through in-depth analysis, we show that MLLMs are particularly underperforming under two aspects: (1) cross-view correspondence for partially occluded views and (2) establishing the coarse camera poses. These findings highlight the necessity of domain-specific refinements or modules that embed stronger multi-view awareness. We believe that our All-Angles Bench offers valuable insights and contribute to bridging the gap between MLLMs and human-level multiview understanding
@article{yeh2025seeing,
title={Seeing from Another Perspective:
Evaluating Multi-View Understanding in MLLMs},
author={Chun-Hsiao Yeh, Chenyu Wang,
Shengbang Tong, Ta-Ying Cheng, Ruoyu Wang,
Tianzhe Chu, Yuexiang Zhai, Yubei Chen,
Shenghua Gao and Yi Ma},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.15280},
year={2025}
}
|
|
| Project Page |
Abstract |
Bibtex |
Preprint |
Code (Coming Soon) |
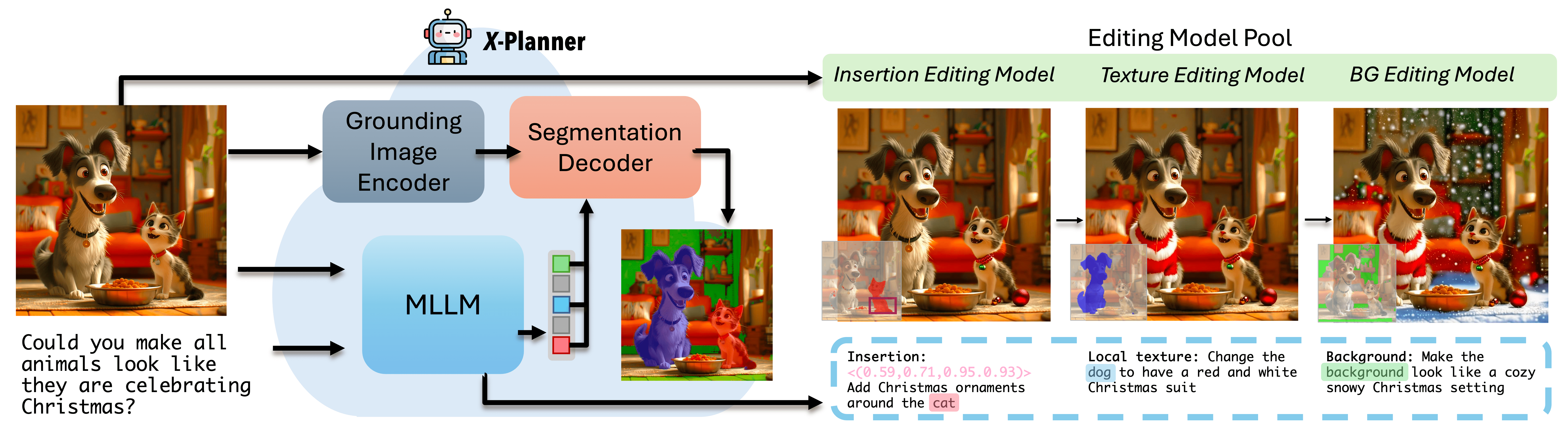
Recent diffusion-based image editing methods have significantly advanced text-guided tasks but often struggle to interpret complex, indirect instructions. Moreover, current models frequently suffer from poor identity preservation, unintended edits, or rely heavily on manual masks. To address these challenges, we introduce X-Planner, a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-based planning system that effectively bridges user intent with editing model capabilities. X-Planner employs chain-of-thought reasoning to systematically decompose complex instructions into simpler, clear sub-instructions. For each sub-instruction , X-Planner automatically generates precise edit types and segmentation masks, eliminating manual intervention and ensuring localized, identity-preserving edits. Additionally, we propose a novel automated pipeline for generating large-scale data to train \textbf{X-Planner} which achieves state-of-the-art results on both existing benchmarks and our newly introduced complex editing benchmark.
@article{yeh2025beyond,
title={Beyond Simple Edits: X-Planner for Complex
Instruction-Based Image Editing},
author={Yeh, Chun-Hsiao and Wang, Yilin and Zhao,
Nanxuan and Zhang, Richard and Li, Yuheng and
Ma, Yi and Singh, Krishna Kumar},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2507.05259},
year={2025}
}
|
|
| Project Page |
Abstract |
Bibtex |
Preprint |
PDF |
Poster |
🤗 Huggingface Model |
Code |
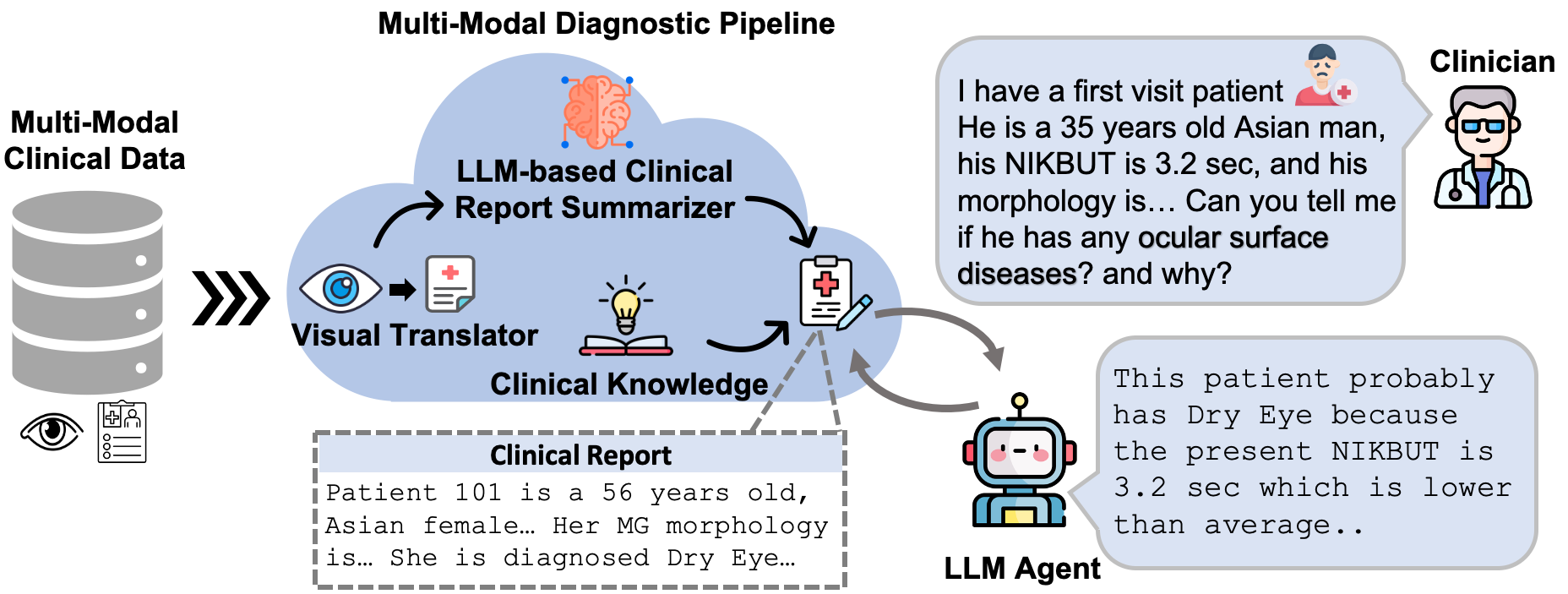
Accurate diagnosis of ocular surface diseases is critical in optometry and ophthalmology, which hinge on integrating clinical data sources (e.g., meibography imaging and clinical metadata). Traditional human assessments lack precision in quantifying clinical observations, while current machine-based methods often treat diagnoses as multi-class classification problems, limiting the diagnoses to a predefined closed-set of curated answers without reasoning the clinical relevance of each variable to the diagnosis. To tackle these challenges, we introduce an innovative multi-modal diagnostic pipeline (MDPipe) by employing large language models (LLMs) for ocular surface disease diagnosis. We first employ a visual translator to interpret meibography images by converting them into quantifiable morphology data, facilitating their integration with clinical metadata and enabling the communication of nuanced medical insight to LLMs. To further advance this communication, we introduce a LLM-based summarizer to contextualize the insight from the combined morphology and clinical metadata, and generate clinical report summaries. Finally, we refine the LLMs' reasoning ability with domain-specific insight from real-life clinician diagnoses. Our evaluation across diverse ocular surface disease diagnosis benchmarks demonstrates that MDPipe outperforms existing standards, including GPT-4, and provides clinically sound rationales for diagnoses.
@inproceedings{yeh2024insight,
title={Insight: A Multi-modal Diagnostic
Pipeline Using LLMs for Ocular Surface
Disease Diagnosis},author={Yeh, Chun-Hsiao
and Wang, Jiayun and Graham, Andrew D and
Liu, Andrea J and Tan, Bo and Chen, Yubei
and Ma, Yi and Lin, Meng C},booktitle=
{International Conference on Medical Image
Computing and Computer-Assisted
Intervention},pages={711--721},year={2024},
organization={Springer}
}
|

|
| Project Page |
Abstract |
Bibtex |
Preprint |
Code |
Recent text-to-image diffusion models are able to learn and synthesize images containing novel, personalized concepts (e.g., their own pets or specific items) with just a few examples for training. This paper tackles two interconnected issues within this realm of personalizing text-to-image diffusion models. First, current personalization techniques fail to reliably extend to multiple concepts --- we hypothesize this to be due to the mismatch between complex scenes and simple text descriptions in the pre-training dataset (e.g., LAION). Second, given an image containing multiple personalized concepts, there lacks a holistic metric that evaluates performance on not just the degree of resemblance of personalized concepts, but also whether all concepts are present in the image and whether the image accurately reflects the overall text description. To address these issues, we introduce Gen4Gen, a semi-automated dataset creation pipeline utilizing generative models to combine personalized concepts into complex compositions along with text-descriptions. Using this, we create a dataset called MyCanvas, that can be used to benchmark the task of multi-concept personalization. In addition, we design a comprehensive metric comprising two scores (CP-CLIP and TI-CLIP) for better quantifying the performance of multi-concept, personalized text-to-image diffusion methods. We provide a simple baseline built on top of Custom Diffusion with empirical prompting strategies for future researchers to evaluate on MyCanvas. We show that by improving data quality and prompting strategies, we can significantly increase multi-concept personalized image generation quality, without requiring any modifications to model architecture or training algorithms.
@article{yeh2024gen4gen,
title={Gen4Gen: Generative Data
Pipeline for Generative Multi-Concept
Composition},author={Yeh, Chun-Hsiao and
Cheng, Ta-Ying and Hsieh, He-Yen and
Lin, Chuan-En and Ma, Yi and Markham,
Andrew and Trigoni, Niki and
Kung, Hsiang-Tsung and Chen, Yubei},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.15504},
year={2024}
}
|

|
| Project Page |
Abstract |
Bibtex |
Preprint |
🤗 Huggingface Demo |
Code |
Creating content for a specific identity (ID) has shown significant interest in the field of generative models. In the field of text-to-image generation (T2I), subject-driven content generation has achieved great progress with the ID in the images controllable. However, extending it to video generation is not well explored. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective subject identity controllable video generation framework, termed Video Custom Diffusion (VCD). With a specified subject ID defined by a few images, VCD reinforces the identity information extraction and injects frame-wise correlation at the initialization stage for stable video outputs with identity preserved to a large extent. To achieve this, we propose three novel components that are essential for high-quality ID preservation: 1) an ID module trained with the cropped identity by prompt-to-segmentation to disentangle the ID information and the background noise for more accurate ID token learning; 2) a text-to-video (T2V) VCD module with 3D Gaussian Noise Prior for better inter-frame consistency and 3) video-to-video (V2V) Face VCD and Tiled VCD modules to deblur the face and upscale the video for higher resolution. Despite its simplicity, we conducted extensive experiments to verify that VCD is able to generate stable and high-quality videos with better ID over the selected strong baselines. Besides, due to the transferability of the ID module, VCD is also working well with finetuned text-to-image models available publically, further improving its usability.
@article{ma2024magic,
title={Magic-Me:
Identity-Specific Video
Customized Diffusion},
author={Ma, Ze and Zhou, Daquan
and Yeh, Chun-Hsiao and
Wang, Xue-She and Li, Xiuyu
and Yang, Huanrui and Dong, Zhen
and Keutzer, Kurt and Feng, Jiashi},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09368},
year={2024}
}
|
|
| Project Page |
Abstract |
Bibtex |
Preprint |
PDF |
Project Video |
Dataset |
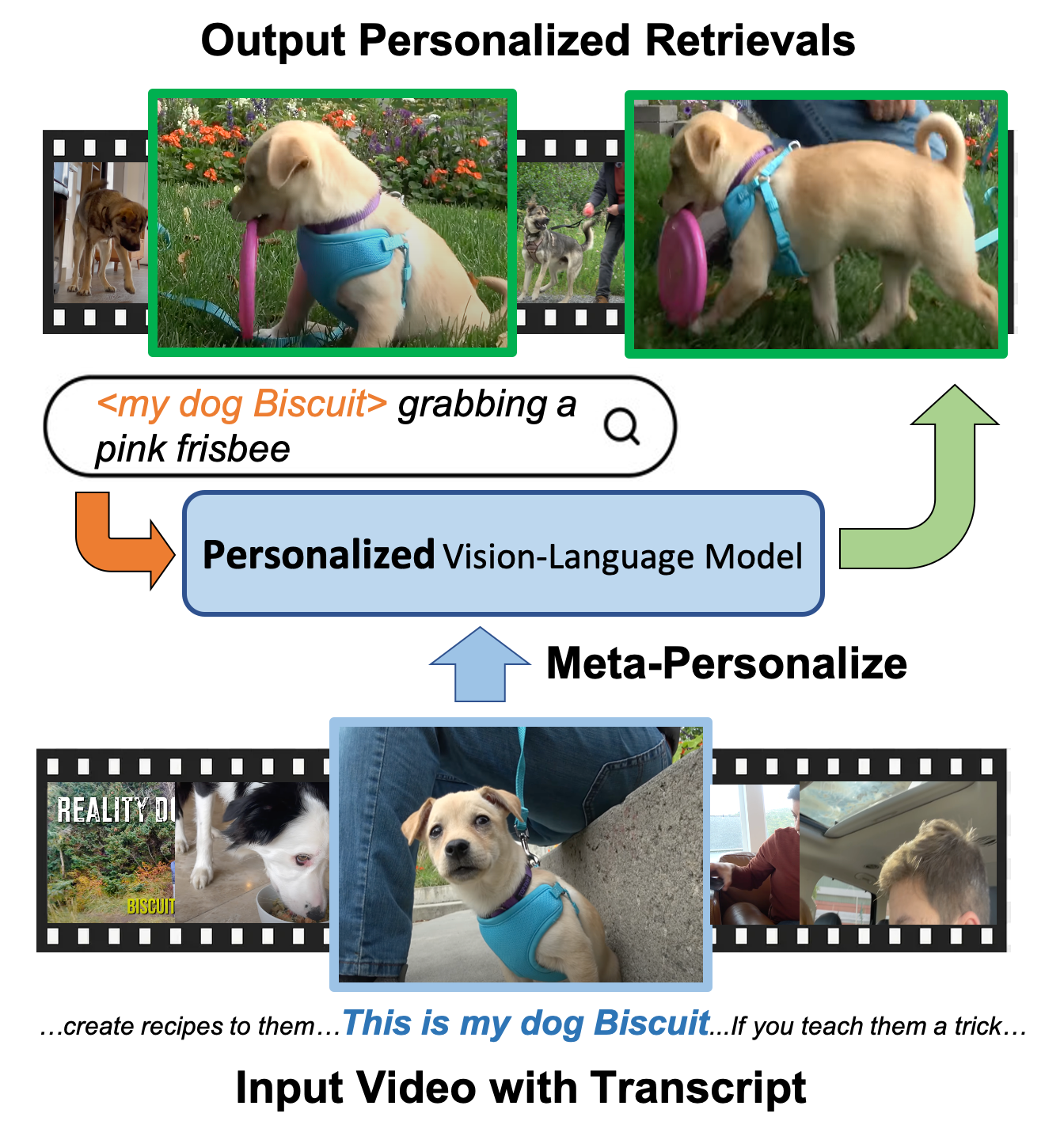
Large-scale vision-language models (VLM) have shown impressive results for language-guided search applications. While these models allow category-level queries, they currently struggle with personalized searches for moments in a video where a specific object instance such as ``My dog Biscuit'' appears. We present the following three contributions to address this problem. First, we describe a method to meta-personalize a pre-trained VLM, learning how to learn to personalize a VLM at test time to search in video. Our method extends the VLM's token vocabulary by learning novel word embeddings specific to each instance. To capture only instance-specific features, we represent each instance embedding as a combination of shared and learned global category features. Second, we propose to learn such personalization without explicit human supervision. Our approach automatically identifies moments of named visual instances in video using transcripts and vision-language similarity in the VLM's embedding space. Finally, we introduce This-Is-My, a personal video instance retrieval benchmark. We evaluate our approach on This-Is-My and DeepFashion2 and show that we obtain a 15% relative improvement over the state of the art on the latter dataset.
@inproceedings{yeh2023meta,
title={Meta-Personalizing
Vision-Language Models To Find Named
Instances in Video},
author={Yeh, Chun-Hsiao and Russell, Bryan
and Sivic, Josef and Heilbron, Fabian Caba
and Jenni, Simon},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition},
pages={19123--19132},
year={2023}
}
|
|
| Abstract |
Bibtex |
Preprint |
PDF |
Project Video |
Code (Lightly-ai) |
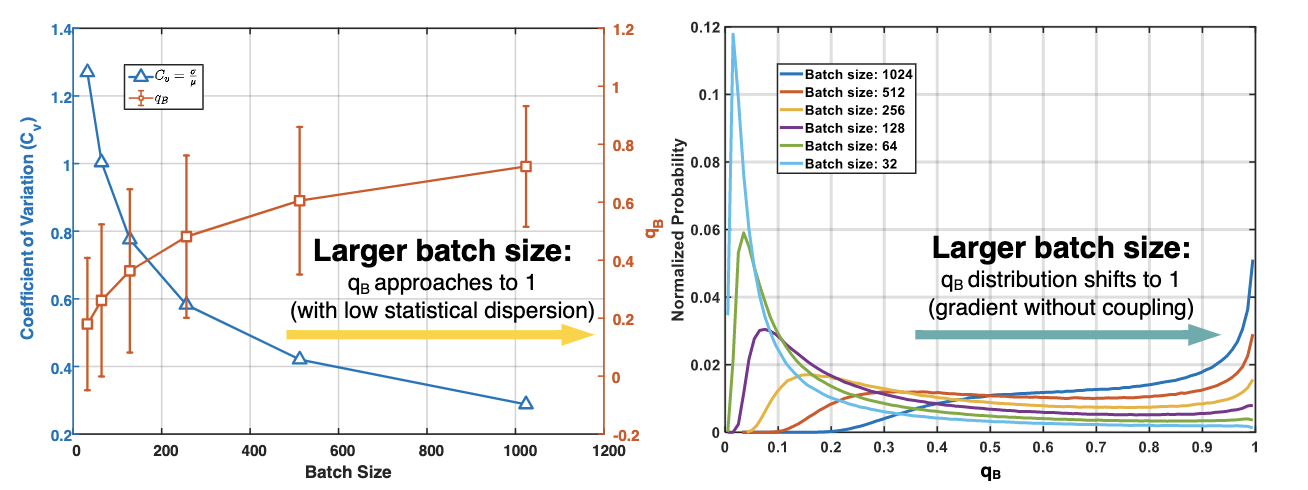
Contrastive learning (CL) is one of the most successful paradigms for self-supervised learning (SSL). In a principled way, it considers two augmented "views" of the same image as positive to be pulled closer, and all other images as negative to be pushed further apart. However, behind the impressive success of CL-based techniques, their formulation often relies on heavy-computation settings, including large sample batches, extensive training epochs, etc. We are thus motivated to tackle these issues and establish a simple, efficient, yet competitive baseline of contrastive learning. Specifically, we identify, from theoretical and empirical studies, a noticeable negative-positive-coupling (NPC) effect in the widely used InfoNCE loss, leading to unsuitable learning efficiency concerning the batch size. By removing the NPC effect, we propose decoupled contrastive learning (DCL) loss, which removes the positive term from the denominator and significantly improves the learning efficiency. DCL achieves competitive performance with less sensitivity to sub-optimal hyperparameters, requiring neither large batches in SimCLR, momentum encoding in MoCo, or large epochs. We demonstrate with various benchmarks while manifesting robustness as much less sensitive to suboptimal hyperparameters. Notably, SimCLR with DCL achieves 68.2% ImageNet-1K top-1 accuracy using batch size 256 within 200 epochs pre-training, outperforming its SimCLR baseline by 6.4%. Further, DCL can be combined with the SOTA contrastive learning method, NNCLR, to achieve 72.3% ImageNet-1K top-1 accuracy with 512 batch size in 400 epochs, which represents a new SOTA in contrastive learning. We believe DCL provides a valuable baseline for future contrastive SSL studies.
@inproceedings{yeh2022decoupled,
title={Decoupled contrastive learning},
author={Yeh, Chun-Hsiao and Hong,
Cheng-Yao and Hsu, Yen-Chi and Liu,
Tyng-Luh and Chen, Yubei and LeCun, Yann},
booktitle={Computer Vision--ECCV 2022:
17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel,
October 23--27, 2022, Proceedings, Part XXVI},
pages={668--684},
year={2022},
organization={Springer}
}
|
|
|
|
Many thanks to webpage, webpage, and website for awesome template. |